How to operate a drone? It’s a question sparking curiosity in many, from hobbyists to professionals. This guide delves into the intricacies of safely and effectively piloting unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced flight maneuvers. We’ll explore the essential controls, navigation techniques, and camera operation, ensuring you gain the confidence and knowledge to take to the skies responsibly.
Understanding the legal framework surrounding drone operation is also crucial, and we’ll address those aspects as well.
This comprehensive guide provides a structured approach to learning, progressing from fundamental safety procedures and basic controls to more advanced techniques and troubleshooting. We’ll equip you with the tools and understanding necessary to enjoy the thrill of drone flight while maintaining a high level of safety and compliance.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before embarking on any drone flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring both safety and operational success. This involves a series of inspections and checks to identify potential issues that could compromise the flight or cause damage. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, equipment damage, and legal repercussions.
Pre-Flight Inspection and Functional Tests
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection involves visually examining the drone for any physical damage, loose parts, or obstructions. This includes checking the propellers for cracks or damage, verifying the battery’s charge level and overall condition, and ensuring all components are securely fastened. Furthermore, a functional test of the motors, GPS signal, and other onboard systems is essential to confirm everything is operating correctly before takeoff.
Sample Pre-Flight Checklist
The following table provides a sample pre-flight checklist. Remember to adapt this to your specific drone model and operational environment.
| Model | Item | Check | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Drone Model] | Battery Charge | Minimum 80% recommended | |
| [Drone Model] | Propeller Condition | Check for cracks or damage | |
| [Drone Model] | GPS Signal Strength | At least 8 satellites are ideal | |
| [Drone Model] | Gimbal Function | Smooth movement, no unusual noises | |
| [Drone Model] | Camera Function | Check video and photo capabilities | |
| [Drone Model] | Motor Function | Test each motor individually | |
| [Drone Model] | Visual Inspection | Check for any physical damage or debris |
Emergency Procedures
Having a plan for emergency situations is paramount. Loss of signal and low battery are two common emergencies. In case of signal loss, the drone should ideally have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If the battery gets low, immediately initiate a controlled descent and landing.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering flight controls. Learning how to safely and effectively pilot your drone is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, responsible drone operation ensures both safety and successful flight experiences.
- Loss of Signal: Engage RTH function if available. If not, attempt to regain signal or perform a controlled emergency landing.
- Low Battery: Immediately initiate a controlled descent and landing. Prioritize a safe landing over completing the flight.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
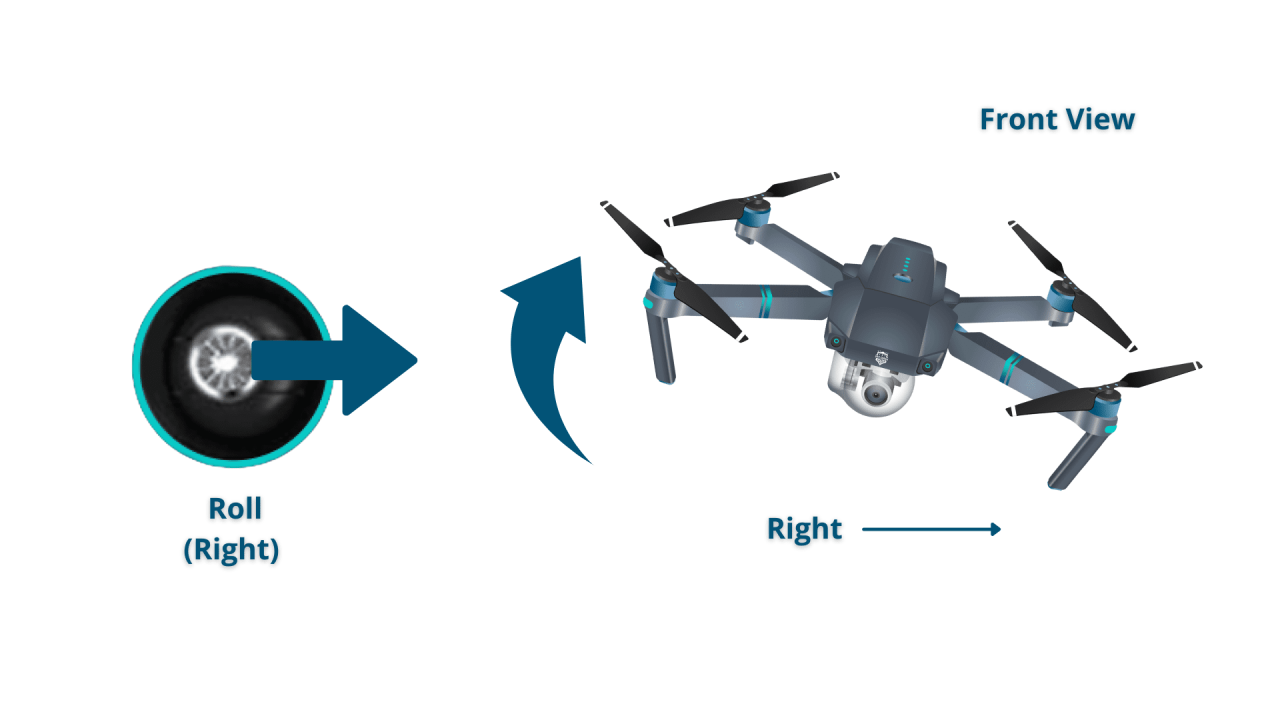
Mastering drone controls is essential for safe and effective operation. Understanding the basic control inputs – throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll – is the foundation for more advanced maneuvers.
Basic Drone Controls
Most drones utilize four primary controls: throttle (controls altitude), yaw (rotates the drone left or right), pitch (moves the drone forward or backward), and roll (moves the drone left or right). The specific mapping of these controls to the controller sticks varies between different control schemes (Mode 1 and Mode 2).
Drone Control Schemes (Mode 1 vs. Mode 2)
Mode 1 and Mode 2 refer to the arrangement of controls on the transmitter. In Mode 1, the left stick controls throttle and yaw, while the right stick controls pitch and roll. In Mode 2, the left stick controls pitch and roll, and the right stick controls throttle and yaw. Familiarizing yourself with your drone’s control scheme is vital before flying.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a good grasp of safety regulations and best practices. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including practical exercises and safety tips, I recommend checking out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. This will help solidify your understanding and ensure safe and responsible drone operation.
Compass and Sensor Calibration
Regular calibration of the drone’s compass and other sensors ensures accurate flight performance and prevents unexpected movements. The calibration process typically involves following on-screen instructions within the drone’s control app. This usually involves moving the drone in specific patterns to allow the sensors to orient themselves.
Tips for Smooth and Controlled Maneuvers
Smooth and precise drone movements require practice and careful control input. Avoid abrupt movements, and use small, incremental adjustments to maintain control. Practice in a wide-open space free of obstacles.
- Use gentle, smooth movements on the control sticks.
- Avoid sudden changes in direction or altitude.
- Practice hovering in place before attempting more complex maneuvers.
Taking Off, Flying, and Landing
Safe and controlled takeoff, flight, and landing procedures are critical for preventing accidents and protecting your drone. These procedures involve a series of steps designed to ensure a smooth and predictable flight experience.
Safe Takeoff Procedure
A safe takeoff involves carefully lifting the drone into the air, ensuring it remains stable and responsive to your controls. Start with a slow, controlled ascent, and always maintain visual contact with the drone.
- Ensure all pre-flight checks are complete.
- Select a clear, open area for takeoff.
- Slowly increase the throttle to lift the drone vertically.
- Maintain visual contact and monitor the drone’s response.
Drone Navigation
Drone navigation involves using a combination of GPS signals and visual cues to guide the drone’s movement. GPS provides location information, while visual cues allow for precise positioning and obstacle avoidance.
Safe Landing Procedure
A safe landing involves a controlled descent and gentle placement of the drone on the ground. Maintain visual contact throughout the landing process and adjust your controls as needed to ensure a smooth landing.
- Select a suitable landing area.
- Slowly decrease the throttle to initiate a controlled descent.
- Maintain visual contact and adjust the controls to compensate for wind or other factors.
- Gently set the drone down on the ground.
Returning to Home Point
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function, which automatically guides the drone back to its takeoff point. This feature is particularly useful in case of signal loss or low battery.
- Activate the RTH function via the drone’s control app.
- Monitor the drone’s return journey.
- Be prepared to take manual control if necessary.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Understanding your drone’s camera features and settings is essential for capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos. This section covers camera specifications, settings adjustments, and tips for optimal image capture.
Drone Camera Features
Drone cameras typically offer a range of features, including resolution (measured in megapixels for photos and frames per second for video), field of view (the angle of view captured by the lens), and video recording capabilities (e.g., 4K, 1080p).
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
Capturing high-quality aerial media requires understanding and adjusting various camera settings. These settings include ISO (sensitivity to light), shutter speed (the duration the shutter stays open), and aperture (the size of the lens opening).
Adjusting Camera Settings

Adjusting camera settings allows for optimization of image quality under different lighting conditions. For example, in bright sunlight, a lower ISO and faster shutter speed are often preferred. In low light, a higher ISO and slower shutter speed might be necessary. Experimentation is key to finding the best settings for your specific conditions.
Optimal Camera Settings for Various Shooting Scenarios
| Scenario | ISO | Shutter Speed | Aperture |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bright Sunlight | 100-200 | 1/500 – 1/2000 | f/5.6 – f/8 |
| Overcast | 200-400 | 1/250 – 1/1000 | f/4 – f/5.6 |
| Low Light | 400-1600 | 1/60 – 1/250 | f/2.8 – f/4 |
| Fast-Moving Subjects | 100-400 | 1/1000 – 1/4000 | f/5.6 – f/8 |
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its continued reliable operation. This includes cleaning, battery care, and addressing common issues.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule should include cleaning the drone’s body and propellers, inspecting for any damage, and properly storing the battery. Cleaning should be done after each flight to remove dirt and debris.
- Clean the drone body and propellers after each flight.
- Inspect the drone for any damage or loose parts.
- Properly store the battery in a cool, dry place.
- Check and tighten all screws and connections.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Understanding common drone problems and their solutions can help you quickly resolve issues and get back to flying. Common problems include motor malfunctions, GPS signal loss, and battery issues.
Troubleshooting Guide
- Problem: Motor malfunction. Solution: Check motor connections, replace damaged motors.
- Problem: GPS signal loss. Solution: Fly in an open area with a clear view of the sky, recalibrate the GPS.
- Problem: Battery issues. Solution: Check battery charge, replace damaged batteries.
- Problem: Propeller damage. Solution: Replace damaged propellers.
- Problem: Camera malfunction. Solution: Check camera connections, restart the drone.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone requires understanding and adhering to local and national regulations. Failure to comply with these regulations can lead to fines, legal action, and even criminal charges.
Importance of Understanding Drone Regulations

Drone regulations vary by location and are designed to ensure safe and responsible operation. Familiarizing yourself with these regulations is crucial before flying.
Key Drone Regulations
Specific regulations vary significantly depending on location (country, state, and even local ordinances). Key aspects often include registration requirements, airspace restrictions (no-fly zones near airports, etc.), and limitations on flight time and distance. Always check your local regulations before operating a drone.
- Registration: Many jurisdictions require drone registration.
- Airspace Restrictions: Avoid flying near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Flight Time and Distance: Adhere to any limitations on flight duration and distance.
- Privacy Concerns: Respect the privacy of others and avoid unauthorized surveillance.
Implications of Violating Drone Regulations
Violating drone regulations can result in significant consequences, including fines, license suspension, and even criminal charges. It’s crucial to understand and comply with all applicable regulations.
Advanced Drone Techniques: How To Operate A Drone
Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can explore advanced drone techniques to enhance your flying skills and capture more creative aerial footage. These techniques require practice and a thorough understanding of your drone’s capabilities.
Advanced Flight Maneuvers
Advanced flight maneuvers, such as flips and rolls, are possible with certain drone models. These maneuvers require precise control and should only be attempted in a safe and open environment after mastering basic flight skills. Always prioritize safety and avoid performing these maneuvers near people or obstacles.
Utilizing Drone Features, How to operate a drone
Many drones offer advanced features like follow-me mode, which allows the drone to automatically follow a subject, and waypoint navigation, which enables you to program a flight path. These features can greatly enhance your flying experience and allow for more creative shots.
Creating and Executing Complex Flight Plans
Creating and executing complex flight plans involves using specialized software or apps to program a series of waypoints and maneuvers. This allows for automated flights, perfect for capturing time-lapses or complex aerial shots. Careful planning and pre-flight checks are essential before executing any complex flight plan.
Advanced Camera Features
Many drones offer advanced camera features, such as cinematic shot modes, which provide pre-programmed camera movements and settings for creating professional-looking footage. Exploring these features can greatly enhance the quality and creativity of your aerial videos.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of pre-flight procedures, flight controls, camera operation, maintenance, and legal considerations. Remember that consistent practice and adherence to safety guidelines are paramount. As you gain experience, explore the advanced techniques to unlock the full potential of your drone and capture breathtaking aerial perspectives.
Safe flying!
FAQ Guide
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and autonomous return-to-home features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with intuitive controls and robust safety features.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes, often less in windy conditions or with heavier payloads.
What happens if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that automatically brings the drone back to its starting point if signal is lost. However, always fly within visual line of sight.
Do I need a license to fly a drone?
Drone regulations vary by location. Some regions require registration and/or licensing for recreational and commercial drone use. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific requirements.
